Dec 13 2021

Dec 10 2021

Dec 07 2021

Dec 02 2021
12B/13B, North Building of Pacific Square, No.331, Jiahe Road, Siming District, Xiamen, Fujian, China. 361001
+86-592-5065811
+8615160739809
Stone knowledge: one-time processing and preparation technology
One-time processing of stone: refers to the whole process of starting from the pretreatment of the blocks and turning the blocks into large slabs through a series of processing.
The basic concept of blocks
Block concept
The stone quarry mined from the rock mass has a certain block shape, good stability, and is trimmed into an approximate rectangular stone blank. The volume of the block is usually 2-10m3, of course, it can also be larger than 10m3. . However, the volume of the blocks is too large and transportation is difficult, and the gantry crane of the factory is difficult to hoist.
1.2 Distinguishing and identifying block surface
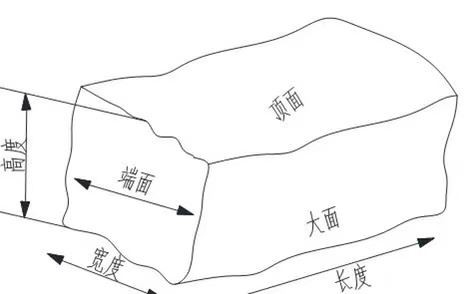
The block is similar to a hexahedron, with six faces: top and bottom; two end faces; two side faces. Usually the two sides (large sides) are the texture of the stone, that is, the opening surface of the block, as shown in Figure 4.
1.2.1 Classification of blocks
According to whether it is natural or not, it is divided into natural stone blocks and non-natural stone blocks;
According to the material, it is divided into marble blocks and granite blocks.
1.3 Measurement of blocks
Length: Measure the length of the block with a tape measure, and determine the length of the block according to the code deduction principle. If the block is regular, the measurement size is reduced by 30mm.
Width: Measure the width of the block with a tape measure, and determine the width of the block according to the code deduction principle. If the block is regular, the measurement size is reduced by 30mm.
Height: Measure the thickness of the block with a tape measure, and determine the thickness of the block according to the code deduction principle. If the block is regular, the measurement size is reduced by 30mm.
Measure the maximum and minimum dimensions in the length, width, and height directions of the block with a steel tape measure. The difference between the maximum size and the minimum size is used to represent the error of length, width, and height. The reading is accurate to 10mm. When measuring the size of the block, the corners, missing edges, blast holes, color spots, color lines, and cracks should also be considered.
1.4 Calculation of block volume and mass
The volume of the block V=length*height*width
The quality of the block=V*ρ
The density of a stone refers to the actual mass per unit volume of the stone. The density of stone mainly depends on the mineral composition of the rock, the size and quantity of pores, and the water content.
The density of granite is generally 2500~3000kg/cubic meter; the density of marble is generally 2600~2800kg/cubic meter. Density is often used to calculate the quality of a block, the quality of the product.
Example: block length is 2.8m, height is 1.6m, width is 1.4m, stone density is 2600kg/m3, mass is M=2.8*1.6.*1.4*2.6*1000=16307kg=16307/1000=
16.3 tons.
1.5 Methods to recognize and inspect blocks
Color, pattern, grain structure. Use visual inspection.
crack. Use visual inspection, water pouring, and hitting.
Color lines, stains. Use a tape measure to measure the length of the color line. Use a tape measure to measure the width of the stain.
Figure 6 shows the production staff inspecting the surface of the blocks using the water-pouring method.
1.6 Stone appearance inspection
(1) Crack
The small gaps in the rock are the most common phenomenon in the stone, especially in the marble. It is difficult to find several types of existing marbles that do not have cracks. The existence of cracks in the stone reduces the utilization rate of the stone. , It increases the difficulty and danger of the production and processing of stone products, and affects the quality of the products. The cracks of the stone can be strengthened by repairing the glue, and the cracks can be repaired.
(2) Color difference (yin and yang color)
The surface of the stone presents another type of color that is inconsistent with the basic color of the stone. This color is completely different from the natural color of the stone. Chromatic aberration is common in beige, serpentine green, coffee and other stones, and granite also has chromatic aberration.
(3) Colors staining
A spot-like substance or strange substance that is different from the basic color of the stone surface.
(4) Hole
There are tiny holes on the surface of some stones, those with a diameter of more than 2mm are called holes.
(5) Color line
Striped and striped substances that are different from the stone surface color and pattern are black, red, white, rusty lines, etc. in the stone. Color lines generally exist in beige and white stones.
1.7 Judgment of the quality of blocks
A: Color
A block of material should be uniform in color from the overall perspective, and there should be no big fluctuations in shades of color, except for individual materials. Judging whether a block has color difference and the severity of the color difference is mainly based on the overall view of the block, and cannot be judged by its parts, otherwise you will not be able to purchase satisfactory and absolutely perfect materials. Natural things are natural. , More or less there are some defects.
B: Crack
Granite must not have cracks, while marble depends on the specific conditions of the material. From the general situation of marble, it is difficult to find several marbles without cracks.
When the crack of the stone belongs to the type of tortoise crack, this kind of material is particularly easy to break, the yield rate must be very low, and there is not much processing value.
When there are cracks in sand and gravel materials, because the sand and gravel materials are loose and easy to break, the glue is not strong, and the sand and gravel stones are generally not allowed to have cracks.
Beige stone is usually allowed to have cracks, but the cracks should not be radial, and it is best to break along the grain.
White stone is generally not allowed to have cracks, especially pure white marble without grain. The repair effect of this pure white marble is difficult to reach a satisfactory level. The white stone that is broken along the grain can be repaired with glue with the same color as the pattern, and the repair effect should be invisible at 1.5 meters from the product.
C: Pattern
The image presented by the composition, structure and structure of decorative stone. The pattern is very important to the stone, and it is an important indicator to measure whether the stone has good decorative properties.
The patterns are divided into straight, twill, chaotic, net, dot, no, landscape, wavy, and spot patterns.
The ruled grain is similar to a straight line, and is approximately parallel to the length or width of the stone. Elephant wood fossils, super white travertine, red travertine;
The diagonal lines make a certain angle with the length or width of the board surface. Such as wood grain yellow, California golden hemp;
The chaotic lines are chaotic, and horizontal lines, straight lines, and diagonal lines intersect. Such as Snow White, Golden Tianlong, Golden Spider, Purple Luohong;
The reticulated lines are like reticulated, such as brown reticulated, light brown reticulated, and large white;
The texture of the landscape is like a stone with a landscape painting. Landscape pattern, big white flowers, cloud ash, dot Cangshan marble;
The wavy pattern resembles water ripples and waves like stone. Such as sea waves, olive green;
There is a crystalline class-like substance on the surface of the dappled stone. Such as blue pearl, green star, brown diamond, etc.;
The dot pattern is the dot-like substance on the surface of the stone. Such as India platinum, snow red, India black gold sand.
The pattern thickness of the stone should be uniform, and the direction should have a certain sense of rules or rhythm, smooth and natural, and avoid ups and downs.
D: Hole
Except for travertine stones, general stones are not allowed to have holes. But travertine stone also has a degree of requirement for holes, not that the bigger the hole, the better. Some dark-colored stones (like deep brown nets) are unrealistic without holes due to the influence of natural factors, and can be determined according to the actual situation of the material.